Doctor of Medicine (MD); 4-year program
-
Duration4 years
-
FeesAED 127,050 (per year)
-
Total # of Credit hours154
Program Overview
Requirements for Admission into the 4-year MD Program (Entry to year three)
- Bachelor’s degree in Medical/Health/Biomedical/Biological/Pharmacological Sciences issued in the UAE or an equivalent degree overseas approved by the Ministry of Education in the UAE. Subjects studied include basic
- Cell biology
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Physics
- Genetics
- Additional preferred subjects studied – pharmacology, pathology, immunology, microbiology, psychology, statistics
- CGPA of 3.0/4 or higher, or its equivalent with official transcripts and graduation certificates certified by the appropriate authorities
- MCAT – minimum score of 500, OR UCAT – minimum score of 2700, OR GAMSAT – minimum score of 63, OR CoM administered MCAT level entrance exam
- A valid certificate of English proficiency as required by the University: IELTS 6.5 / TOEFL IBT score of 79 or its equivalent
- Personal Interview
Program Learning Outcomes
On successful completion of the MD program, graduates will be able to:
KNOWLEDGE
K1. Recognize the normal structure and function of the human body (as an intact organism) and of each of its major organ systems, taking cognizance of the molecular, biochemical, and cellular mechanisms that are important in maintaining the body’s homeostasis.
K2. Recognize and relate the various causes (genetic, developmental, metabolic, toxic, microbiologic, autoimmune, neoplastic, degenerative, and traumatic) of illness/disease and the ways in which they interfere with normal function of the body (pathogenesis).
K3. Recognize the altered structure and function (pathology and pathophysiology) of the body and its major organ systems that are seen in various diseases and conditions.
K4. Recognize the important non-biological determinants of health and of the economic, psychological, social, and cultural factors that contribute to the development and/or continuation of disease.
K5. Identify the most frequent clinical, laboratory, radiological, and pathologic manifestations of common diseases.
K6. Recognize the power of “the scientific method” in establishing the causation of disease and efficacy of traditional and non-traditional therapies.
K7. Describe the principles of disease prevention and epidemiology of common diseases appropriate for specific populations.
K8. Demonstrate knowledge of the laws and systems of professional regulation through the UAE Ministry of Health, relevant to medical practice and abide by the UAE’s Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct.
K9. Understand the framework in which medicine is practiced in the UAE, and the roles of, and relationships between the MOH, Health Authorities and the private health sector in protecting and promoting individual and population health.
SKILL
S1. The ability to obtain an accurate holistic medical history that covers all essential aspects of a patient and his/her problem, including issues related to age, gender and socio-economic status.
S2. Apply a medical problem-solving process in order to arrive at a clinical diagnosis.
S3. Perform both a complete and a focused organ system specific examination, including a mental status examination.
S4. Perform routine technical procedures at a level suitable to a fresh medical graduate.
S5. Construct appropriate management strategies (both diagnostic and therapeutic) for patients with common conditions related to different age groups and genders, both acute and chronic, including medical, psychiatric, and surgical conditions, and those requiring short- and long-term rehabilitation.
S6. Formulate a treatment plan, demonstrating the ability to take action by balancing the relative risks and benefits of outcomes and treatment options.
S7. Recognize patients with immediately life threatening cardiac, pulmonary, or neurological conditions regardless of etiology, and to institute appropriate initial therapy applying Basic Life Support and Advanced Life Support principles.
S8. Interpret laboratory tests (recognizing their limitations), and integrate clinical and laboratory findings in the diagnosis and management of a patient’s problem.
S9. Document and share patient-specific information, demonstrating the ability to record in the hospital management systems, specific findings about a patient and orders directing the further care of the patient.
S10. Define and describe the characteristics of a population, to include its demography, cultural and socioeconomic constitution, circumstances of living, and health status, and to relate these factors to the health and health care of patients and their families.
S11. Recognize own personal and professional limits and seek help from colleagues and supervisors when necessary.
COMPETENCE
Autonomy and Responsibility (CA)
-
Acquire, assess, apply and integrate new knowledge, learn to adapt to changing circumstances and ensure that patients receive the highest level of professional care.
-
Show responsibility and independent technical and clinical decision-making to evaluate and manage complex and unpredictable clinical work appropriate to a primary care practice.
-
Illustrate adherence to current best practice methods in a mature manner.
Role in Context (CR)
-
Function effectively as a mentor and teacher including contributing to the appraisal, assessment and review of colleagues, giving effective feedback, and taking advantage of opportunities to develop these skills.
-
Understand and respect the roles and expertise of health and social care professionals in the context of working and learning as an interdisciplinary team.
-
Demonstrate ability to build team capacity and positive working relationships and undertake various team roles including leadership and the ability to accept leadership by others.
-
Demonstrate awareness of the role of doctors as managers, including seeking ways to continually improve the use and prioritization of resources.
Self-development (CS)
-
Establish the foundations for lifelong learning and continuing professional development appropriate to a fresh medical graduate.
-
Continually and systematically reflect on practice to evaluate and improve care of patients with aim of safeguarding a high quality of clinical care.
-
Recognize own personal health needs, consult and follow the advice of a suitably qualified professional, and protect patients from any risk posed by own health.
-
Value professional ethics, positive criticism and feedback, and engage in a life-long learning.
-
Be polite, considerate, trustworthy and honest, act with integrity, maintain confidentiality, respect patients’ dignity and privacy, and understand the importance of appropriate consent and respect all patients, colleagues and others regardless of their age, colour, religion, culture, disability, ethnic or national origin, gender, or social or economic status.
Program Structure and Credit Hours
CURRICULUM DESCRIPTION
Our program is 4-year long and runs in two serial phases as follows:
- Phase II - Two years of Pre-clerkships (Years 3 and 4) – consisting mainly of weekly disease-anchored Problem-Based Learning (PBL) type blocks covering all the systems. The robust clinical skills program runs in parallel with all the blocks. Other longitudinal (parallel) courses are offered, including courses like biostatistics and epidemiology, primary and rural health and family medicine, health informatics, economics and management, behavioral sciences, addiction and substance use, and research. The phase culminates in an integrated multisystem block at the end of year 4 to help the students prepare for the IFOM Basic Science Exam as mandated by the CAA.
- Phase III - Two years of Clerkships (Years 5 and 6) – consisting of 20-week semesters over the two years and an additional six weeks of clinical electives during the summer of between year 5 and year 6. Students are expected to sit for the IFOM Clinical Science Exam by the end of year 6 as mandated by the CAA.
Our program is designed as an integrated, system-based, spiral curriculum, which is divided into two phases. There is both horizontal and vertical integration such that as the student progresses through the phases, they revisit the same organ systems at higher levels of complexity and clinical content until graduation.
A unique feature of the AUCoM curriculum is the application of “Parallel Courses”. These are semester long courses running alongside (parallel to) the integrated blocks. In many instances, the parallel courses align their content to the running blocks. Parallel courses address one of the main criticisms in integrated PBL-type curricula; the niggling feeling that the students are not learning core concepts in sufficient depth. A secondary advantage of the parallel courses is that the program has greater flexibility in formally introducing new or topical subjects into the curriculum, e.g. simple one or two credit hour courses in Health Informatics, Economics, and Management, and Addiction and Substance Use, etc. has potential to greatly enrich the curriculum. Such flexibility is lacking or limited in the common integrated curricula on offer at most medical schools in the region. Experience at a young medical school (<10 years), applying a similar mix of integrated and parallel courses has produced graduates who are exceptionally competitive in external benchmarking and licentiate assessments.
Study Plan
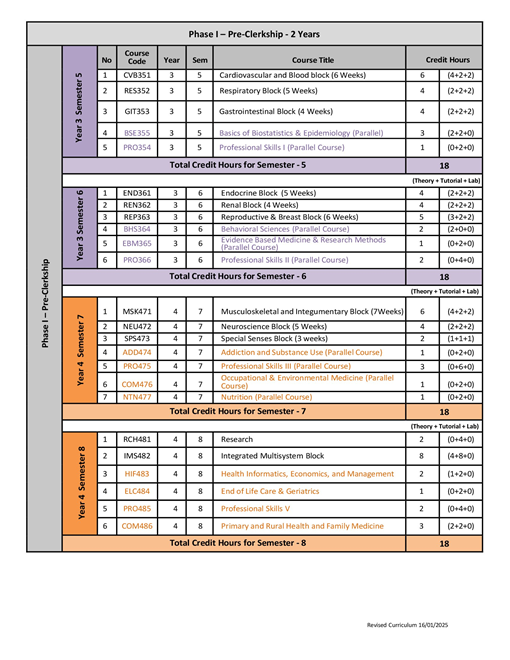
Courses Descriptions
Phase II – Pre-Clerkships
CVB351 Cardiovascular and Blood block
This is an interdisciplinary, integrated, problem-based module of the cardiovascular and blood system, comprehensively correlating basic knowledge about the structure and function of the heart, vascular tree, and blood to the clinical manifestations of disease states. Calendar weeks are divided into themes of clinical interest. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning objectives of that theme. The pathogenic origins of disease states of the cardiovascular and blood system are thoroughly dissected. Students are then provided with the skills and competencies necessary to develop an effective management plan of the common disorders. A Clinical Simulation activity runs concurrently, exposing students to real-life clinical scenarios related to the module, and acquainting them with the examination, diagnosis, and management approaches to these clinical presentations.
RES352 Respiratory Block
This is an interdisciplinary, integrated, problem-based module of the respiratory system, comprehensively correlating basic knowledge about the structure and function of the lungs to clinical manifestations of disease states. Calendar weeks are divided into themes of clinical interest. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning objectives of that theme. The pathogenic origins of disease states of the respiratory system are thoroughly dissected. Students are then provided with the skills and competencies necessary to develop an effective management plan of the common pulmonary disorders. A Clinical Simulation activity runs concurrently, exposing students to real-life clinical scenarios related to the module, and acquainting them with the examination, diagnosis, and management approaches to these clinical presentations.
GIT353 Gastrointestinal Block
This is an interdisciplinary, integrated, problem-based module of the gastrointestinal system, comprehensively correlating basic knowledge about the structure and function of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts to clinical manifestations of disease states. Calendar weeks are divided into themes of clinical interest. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning objectives of that theme. The pathogenic origins of disease states of the gastrointestinal system are thoroughly dissected. Students are then provided with the skills and competencies necessary to develop an effective management plan of the common disorders of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts. A Clinical Simulation activity runs concurrently, exposing students to real-life clinical scenarios related to the module, and acquainting them with the examination, diagnosis, and management approaches to these clinical presentations.
BSE354 Basics of Biostatics & Epidemiology
This course introduces the student to epidemiology and to epidemiologic approach to problems of health and disease. The basic principles and methods of epidemiology are presented together with many applications of epidemiology to public health and clinical practice. This course explores fundamental concepts and methods of statistics as applied to health-related fields. Moreover, the student will be acquainted with most statistical techniques needed in research. The students will demonstrate their learning through: regular attendance, classroom discussions, practical exercises, reports, course assignments and exams.
PRO355 Professional Skills I
This is a semester-long course. It runs parallel to the three blocks of semester: Cardiovascular and Blood (6 weeks), Respiratory (5 weeks), and Gastrointestinal (4 weeks). Each block contains target skill sets which have been selected as a key foundation for acquisition of medical students. The course assists the students to integrate critical thinking with practical skills by means of developing connections between basic science knowledge and clinical presentations. Training involves: History Taking, symptomatology recognition, physical examination, common diagnostic methods and the acquisition and deployment of necessary procedural skills related to the system blocks.
END361 Endocrine Block
This is an interdisciplinary, integrated, problem-based module of the endocrine system, comprehensively correlating basic knowledge about the structure and function of the endocrine glands to clinical manifestations of disease states. Calendar weeks are divided into themes of clinical interest. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning objectives of that theme. The pathogenic origins of disease states of the endocrine system are thoroughly dissected. Students are then provided with the skills and competencies necessary to develop an effective management plan of the common endocrinology disorders of the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreatic, and adrenal glands. A Clinical Simulation activity runs concurrently, exposing students to real-life clinical scenarios related to the module, and acquainting them with the examination, diagnosis, and management approaches to these clinical presentations.
REP362 Reproductive & Breast Block
This is an interdisciplinary, integrated, problem-based module of the reproductive system, comprehensively correlating basic knowledge about the structure and function of the reproductive organs and the breast to clinical manifestations of disease states. Calendar weeks are divided into themes of clinical interest. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning objectives of that theme. The pathogenic origins of disease states of the reproductive system are thoroughly dissected. Students are then provided with the skills and competencies necessary to develop an effective management plan of the common disorders of the male and female reproductive organs. A Clinical Simulation activity runs concurrently, exposing students to real-life clinical scenarios related to the module, and acquainting them with the examination, diagnosis, and management approaches to these clinical presentations.
REN363 Renal Block
This is an interdisciplinary, integrated, problem-based module of the urinary tract, comprehensively correlating basic knowledge about the structure and function of the kidney to clinical manifestations of disease states. Calendar weeks are divided into themes of clinical interest. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning objectives of that theme. The pathogenic origins of disease states of the urinary tract are thoroughly dissected. Students are then provided with the skills and competencies necessary to develop an effective management plan of the common nephrology and urology disorders. A Clinical Simulation activity runs concurrently, exposing students to real-life clinical scenarios related to the module, and acquainting them with the examination, diagnosis, and management approaches to these clinical presentations.
BHS364 Behavioral Science
The main aim of integrated public health teaching is to facilitate the students’ acquisition of knowledge, skills and attitudes that allow them to understand the bases of human behavior, and use those principles for the benefit of medical practice. The goal of this semester long parallel course is to introduce second year medical students to the field of Behavioral Science, by highlighting its fundamental principles and theories. In this regard, students will feel capacitated to approach psychological problems that are common in everyday medical situations.
PRO365 Professional Skills II
This is a semester-long course. It runs parallel to the three blocks of semester: Endocrine (5 weeks), Reproductive and Breast (6 weeks), and Renal (4 weeks). Each block contains target skill sets which have been selected as a key foundation for acquisition of medical students. The course assists the students to integrate critical thinking with practical skills by means of developing connections between basic science knowledge and clinical presentations. Training involves: History Taking, symptomatology recognition, physical examination, common diagnostic methods and the acquisition and deployment of necessary procedural skills related to the system blocks.
COM366 Evidence Based Medicine & Research
Scientific research plays an important role in our efforts to maintain health and combating diseases. This course aims at equipping students with basic knowledge and skills of research methodology using different epidemiological methods. Moreover, this course is concerned with learning about research design and using evidence in clinical research. The course will also address the critical appraisal of published evidence: encouraging students to become ‘literate’ in the use of evidence to shape their practice.
MSK471 Musculoskeletal and Integumentary Block
This is an interdisciplinary, integrated, problem-based module of the musculoskeletal and skin system, comprehensively correlating basic knowledge about the structure and function of bones, joints, muscles, and associated soft tissues to clinical manifestations of disease states. Calendar weeks are divided into themes of clinical interest. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning objectives of that theme. The pathogenic origins of disease states of the musculoskeletal and skin system are thoroughly dissected. Students are then provided with the skills and competencies necessary to develop an effective management plan of the common disorders of bones, muscles, joints, and soft tissues. A Clinical Simulation activity runs concurrently, exposing students to real-life clinical scenarios related to the module, and acquainting them with the examination, diagnosis, and management approaches to these clinical presentations.
NEU472 Neuroscience Block
This is an interdisciplinary, integrated, problem-based module of the nervous system, comprehensively correlating basic knowledge about the structure and function of the central and peripheral nervous systems to clinical manifestations of disease states. Calendar weeks are divided into themes of clinical interest. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning objectives of that theme. The pathogenic origins of neurological and psychiatric disease states are thoroughly dissected. Students are then provided with the skills and competencies necessary to develop an effective management plan of the common disorders of bones, muscles, joints, and soft tissues. A Clinical Simulation activity runs concurrently, exposing students to real-life clinical scenarios related to the module, and acquainting them with the examination, diagnosis, and management approaches to these clinical presentations.
SPS473 Special Senses Block
The Special Senses block is covering normal structure and function as well as integrating disease processes and pharmacotherapy of the diseases related to special senses organs. In addition, a clinical skills program runs concurrently, teaching the students the skills required for examination and diagnostic approach to different clinical presentations in ophthalmic and otolaryngologic disorders. The course runs over three weeks. All the learning activities are centred on weekly themes. A typical week starts with the teaching of structure and function followed by disease processes and pharmacotherapy. In the last part of the week clinical lectures are delivered to relate clinical features with the disease processes, and to discuss diagnostic approaches to different clinical presentations. A PBL case relevant to the theme of the week is discussed and serves to anchor the learning around that theme. The contents of the block will be delivered through multiple formats as appropriate.
ADD474 Addiction and Substance Use
This is a 1-credit-hour course which focuses on the biopsychosocial and treatment aspects of addiction. The course will focus on the neurobiology of addiction, the epidemiology of substance use and behavior addiction and to learn the difference between dependence and substance use disorders (SUD). Best practices and treatment of SUDs with different medications in addition to psychosocial approaches will be taught. Collaborative care approach will be taught so students are better prepared. It will also address potential misuse, relapse, and safer use, as well as caring for pregnant women and other special populations with SUD. Moreover, the course will address co-occurring psychiatric disorders as well as preventing and treating overdose.
PRO475 Professional Skills III
This is a semester-long course. It runs parallel to the three blocks of semester: Musculoskeletal and Integumentary (7 weeks), Neuroscience (5 weeks), and Special Senses (3 weeks). Each block contains target skill sets which have been selected as a key foundation for acquisition of medical students. The course assists the students to integrate critical thinking with practical skills by means of developing connections between basic science knowledge and clinical presentations. Training involves: History Taking, symptomatology recognition, physical examination, common diagnostic methods and the acquisition and deployment of necessary procedural skills related to the system blocks.
COM476 Occupational & Environmental Medicine
This course introduces the student to the interaction between humans and the environment, including workplace environment, and how this interaction affects the health of individuals and communities. It includes an overview of the physical, chemical and biological hazards found in the environment and the health risks associated with workplace and community exposure to them. Major global environmental and occupational health issues, and specific issues in UAE, will be discussed, as well as the approaches taken to address them, and the challenges that must be overcome to ensure success in dealing with them. The students will demonstrate their learning through: regular attendance, classroom discussions, field visits, reports, course assignments and exams.
NTN477 Nutrition
Basic facts and principles of human nutrition are presented. Study includes the physiological and psychological factors of food intake and utilization with emphasis on nutrition education for dietary improvements of groups and individuals. Emphasis is placed on the science of nutrition, the study of nutrients and of their ingestion, digestion, absorption, transport, metabolism, interaction, storage and excretion. Food group plans, the Dietary Guidelines, Food Exchange System, Recommended Dietary Allowances and other standards are reviewed to serve as a foundation for food selection.
RCH481 Research
This is a 2-credit-hour course which focuses on research project, presentation, and report writing. During Year 3 Semester 6, students will be presented with the concepts research methodology in a designated course (Evidence-based Medicine and Research Methods). Students will be required to sign up for research projects with faculty at AUCoM or with Adjunct Faculty of the affiliated teaching hospitals and commence their research projects for a duration of 1 year. During Year 4 Semester 8, students will be required to complete their research projects, give a presentation and prepare a research report for assessment in this course. It is strongly encouraged that the students publish their research results by the end of this semester.
IMS482 Integrated Multisystem Block
This 8-credit hour, semester-long course will be offered during Pre-clerkship Year 2 (Year 4 of the program). The course content will be integrated around multi-organ system clinical cases, building on a multidisciplinary approach to topics from the previous courses that will require critical thinking and clinical problem-solving skills. The key instructional strategies will include large group interactive lecturing, and small group problem-based and team-based learning.
The main underlying aim of this course is to prepare students for the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME) International Foundation of Medicine (IFOM), and the United States Medical Licensure Examinations (USMLE). As mandated by the CAA, a percentage of the official IFOM scores will contribute towards the summative assessment of the Integrated Multisystem course.
HIF483 Health Informatics, Economics, and Management
In consideration of their overarching themes and concepts, two separate, parallel courses on "Medical Informatics", and "Health Economics and Management" were merged into a single, 2-credit-hour course. The course will cover the principles and applications of health informatics, information systems, and technology to translational science. Students will gain a deeper understanding of health financing through in-depth case studies of health systems and health care management, and by reviewing present and future strategic issues of the healthcare industry to propose policy solutions to emergent challenges. Key instructional strategies include interactive lectures, problem-based, and case-based learning.
ELC356 End of Life Care and Geriatrics
Geriatric care provides an opportunity to explore a field of health care that focuses on the care of older adults. The course aims to teach medical students to apply specific skills required for the need assessment, treatment and management of the elderly. Challenges encountered in this specific group of patients with regards to communication, diagnosis, and management will be particularly dissected and emphasized. The students will demonstrate their learning through: regular attendance, classroom discussions, field visits, reports, course assignments and exams.
PRO485 Professional Skills IV
This is a semester-long course that runs parallel to the Integrated Multisystem Block (IMS482). Revision of target professional and clinical skill sets is provided. The course assists the students to integrate critical thinking with practical skills by means of developing connections between basic science knowledge and clinical presentations. Training involves: History Taking, symptomatology recognition, physical examination, common diagnostic methods and the acquisition and deployment of necessary procedural skills related to the various system blocks.
COM486 Primary and Rural Health and Family Medicine
The “Primary Healthcare and Rural Health” and “Family Medicine” courses were combined into a single 3-credit-hour course in light of their overarching themes. Through interactive lectures, problem-based learning and case-based discussions, this course aims to equip the students with the knowledge of the specialty, including understanding its principles and foundations in the basic medical sciences and evidence-based research. Students will be able to identify, diagnose and treat acute or chronic; single or multi-system diseases with appropriate prioritization of patient problems and resources available in primary and rural healthcare settings.
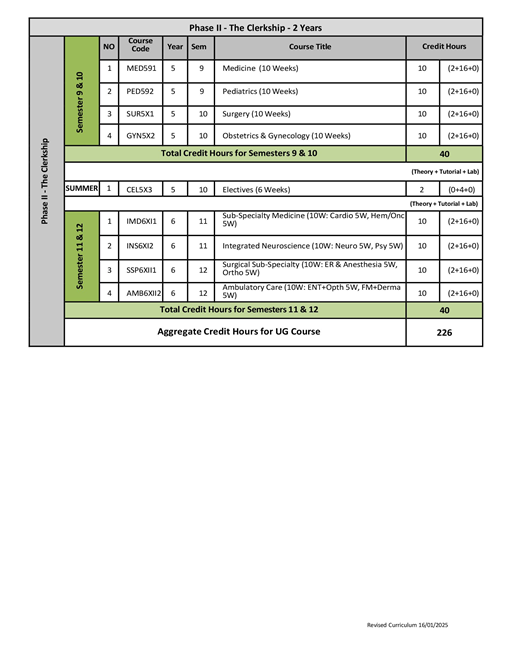
Phase III – Clerkships
MED591 Medicine
This core clerkship is designed to develop clinical competence, to foster appropriate attitudes toward professional responsibility as a physician, and to introduce students to the specialty of Internal Medicine. The medical clerkship is a 10-week rotation offered at our affiliated teaching hospitals. Learning will be primarily patient-oriented. Students devote 80% of their time evaluating medical patients in the allocated hospitals at both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings, with the remaining 20% assigned for didactic teaching and seminars. By the end of the clerkship, students are expected recognize and understand the common medical conditions as well as the emergency medical presentations, and to identify the clinical approach to the diagnosis and the recommended management plans. Faculty instructions and supervision are commenced on daily basis by bedside tutoring and case-based discussions. A clinical skill component runs on weekly basis in the Clinical Simulation Center to complement the bedside teaching.
PED592 Pediatrics
This core clerkship is designed to develop clinical competence, to foster appropriate attitudes toward professional responsibility as a physician, and to introduce students to the specialty of Pediatrics. The pediatrics clerkship is a 10-week rotation offered at our affiliated teaching hospitals. Students devote 80% of their time evaluating pediatric patients in the allocated hospitals at both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings, with the remaining 20% assigned for didactic teaching and seminars. By the end of the clerkship, students are expected recognize and understand the common conditions as well as the emergency presentations in pediatrics, and to identify the recommended management plans. Faculty instructions and supervision are commenced on daily basis by bedside tutoring and case-based discussions. A clinical skill component runs on weekly basis in the Clinical Simulation Center to complement the bedside teaching.
SUR5X1 Surgery
This core clerkship is designed to develop clinical competence, to foster appropriate attitudes toward professional responsibility as a physician, and to introduce students to the specialty of General Surgery. The surgical clerkship is a 10-week rotation offered at our affiliated teaching hospitals. Students devote 80% of their time evaluating surgical patients in the allocated hospitals at both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings, with the remaining 20% assigned for didactic teaching and seminars. By the end of the clerkship, students are expected recognize and understand the common surgical conditions as well as the emergency surgical presentations, and to identify the recommended management plans. Preoperative optimization and postoperative course in surgical conditions will be emphasized. Faculty instructions and supervision are commenced on daily basis by bedside tutoring and case-based discussions. A clinical skill component runs on weekly basis in the Clinical Simulation Center to complement the bedside teaching.
GYN5X2 Obstetrics and Gynecology
This core clerkship is designed to develop clinical competence, to foster appropriate attitudes toward professional responsibility as a physician, and to introduce students to the specialty of OBGYN. The OBGYN clerkship is a 10-week rotation offered at our affiliated teaching hospitals. Students devote 80% of their time evaluating obstetric and gynecologic patients in the allocated hospitals at both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings, with the remaining 20% assigned for didactic teaching and seminars. By the end of the clerkship, students are expected recognize and understand the common conditions as well as the emergency presentations of obstetrics and gynecology, and to identify the recommended management plans. Students will establish a solid foundation of skills and knowledge in women’s health, which will be both applicable and important in any potential future career choice. Faculty instructions and supervision are commenced on daily basis by bedside tutoring and case-based discussions. A clinical skill component runs on weekly basis in the Clinical Simulation Center to complement the bedside teaching.
CEL5X3 Elective Course
The elective clinical course is designed to offer the students the opportunity to be exposed to other healthcare systems, preferably outside the country, in a specialty/training field of their choice. The course aids most undergraduate students in gaining clear insight into their future postgraduate specialty and allows them to actively engage in clinical practice and to apply their knowledge. This is a 6-week long course offered during the interface between year 5 and year 6.
IMD6XI1 Sub-Specialty Medicine
The sub-specialty medical clerkship is a 10-week rotation offered at our affiliated teaching hospitals. Learning will be primarily patient-oriented. Students devote 80% of their time evaluating medical patients in the allocated hospitals at both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings, with the remaining 20% assigned for didactic teaching and seminars. The course expands knowledge, skills, and competencies in the following subspecialties; Cardiology, Pulmonary and Critical care Medicine, and Hematology and oncology. Faculty instructions and supervision are commenced on daily basis by bedside tutoring and case-based discussions. A clinical skill component runs on weekly basis in the Clinical Simulation Center to complement the bedside teaching.
INS6X12 Integrated Neuroscience
The Integrated Neuroscience clerkship is a 10-week rotation offered at our affiliated teaching hospitals. Learning will be primarily patient-oriented. Students devote 80% of their time evaluating medical patients in the allocated hospitals at both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings, with the remaining 20% assigned for didactic teaching and seminars. The course expands knowledge, skills, and competencies in the following subspecialties; Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. Faculty instructions and supervision are commenced on daily basis by bedside tutoring and case-based discussions. A clinical skill component runs on weekly basis in the Clinical Simulation Center to complement the bedside teaching.
SSP6XI1 Surgical Sub-Specialty
The Surgical Sub-specialty clerkship is a 10-week rotation offered at our affiliated teaching hospitals. Learning will be primarily patient-oriented. Students devote 80% of their time evaluating medical patients in the allocated hospitals at both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings, with the remaining 20% assigned for didactic teaching and seminars. The course expands knowledge, skills, and competencies in the following subspecialties; Emergency and Anesthesia, Trauma and Orthopedics. Faculty instructions and supervision are commenced on daily basis by bedside tutoring and case-based discussions. A clinical skill component runs on weekly basis in the Clinical Simulation Center to complement the bedside teaching.
AMB6XI2 Ambulatory Care
The Ambulatory Care clerkship is a 10-week rotation offered at our affiliated teaching hospitals. Learning will be primarily patient-oriented. Students devote 80% of their time evaluating medical patients in the allocated hospitals at both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings, with the remaining 20% assigned for didactic teaching and seminars. The course expands knowledge, skills, and competencies in the following subspecialties; ENT and Ophthalmology, Family Medicine, and Dermatology. Faculty instructions and supervision are commenced on daily basis by bedside tutoring and case-based discussions. A clinical skill component runs on weekly basis in the Clinical Simulation Center to complement the bedside teaching.